导航栏
"QAIT" focuses on the fields of intelligent perception and smart monitoring, deeply integrating IoT and AI technologies to provide full-chain park platform services for scenarios such as smart cities, smart parks, smart transportation, and smart communities. By building a multi-dimensional perception network and an intelligent central system, it realizes cross-domain data interconnection and AI visual analysis, enabling rapid and accurate responses to needs such as public safety and emergency command. Meanwhile, leveraging technologies like digital twin and big data modeling, it optimizes the operation and management of cities and parks, improves energy utilization efficiency and service experience, and helps create a safe, efficient, and intelligent digital ecosystem.
1.Smart Monitoring Overview
"Smart monitoring" is an intelligent monitoring system that integrates advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, big data, and cloud computing. It aims to achieve precise perception, real-time analysis, and intelligent decision-making for people, objects, and scenarios.
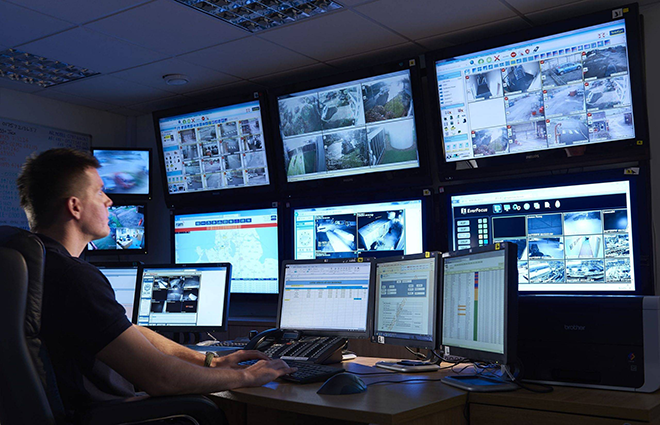

Smart Monitoring
2.Core Technical Support
(1)Artificial Intelligence(AI):
Computer vision: Through technologies such as image recognition, object detection (e.g., YOLO algorithm), and behavior analysis, it realizes real-time recognition of people, vehicles, and objects in surveillance footage (such as facial recognition and license plate recognition) and early warning of abnormal behaviors (such as fights and item abandonment).
Machine learning: Utilizes historical data to train models, enhancing the monitoring system's ability to judge complex scenarios (such as predicting peak pedestrian flow in areas and identifying potential safety hazards).

Artificial Intelligence Camera
(2)Internet of Things(IoT):
Combining devices such as sensors (e.g., infrared, temperature/humidity, smoke sensors), cameras, and RFID tags, it constructs a "connected things" monitoring network to achieve real-time collection of environmental data (e.g., temperature, gas concentration) and object status (e.g., equipment operation parameters).
(3)Big Data and Cloud Computing:
Massive monitoring data is stored and processed through a cloud computing platform, supporting real-time analysis, historical data retracing, and trend prediction (such as optimizing the deployment of security personnel by analyzing passenger flow data in parks).
(4)Communication Technology:
High-bandwidth and low-latency communication capabilities ensure high-definition transmission and real-time response of monitoring videos, which is particularly suitable for scenarios such as remote monitoring and emergency command.
3.Typical Application Scenarios
(1)Smart City:
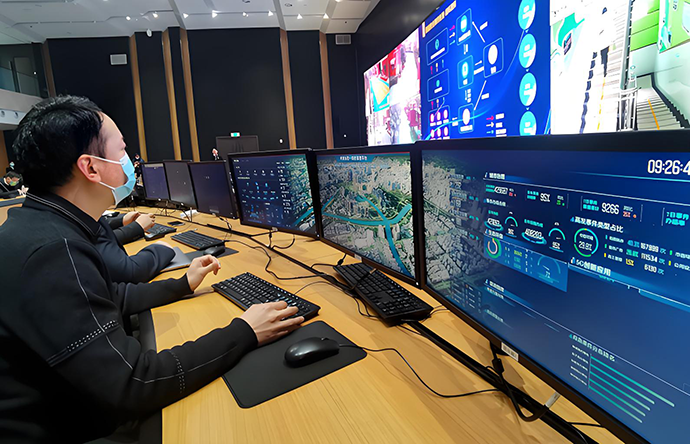

Smart City
Public Safety: Deploy intelligent cameras in public places such as traffic intersections, shopping malls, and stations to monitor suspicious persons or behaviors (such as tailgating and crowd gathering) in real time, and link with the public security system for quick response.
Traffic management: Optimize traffic light timing through video analysis, identify traffic violations (such as running red lights and illegal parking), and achieve intelligent traffic guidance by integrating vehicle networking data.
Urban management: Monitor manhole cover movement, abnormal river water levels, garbage overflow, etc., automatically trigger warnings through IoT sensors, and improve urban operation and maintenance efficiency.
(2)Smart Park (Factory/Campus/Office Building):
Work safety: Deploy monitoring systems in factory workshops to identify risks in real time, such as workers not wearing safety helmets and abnormal equipment operation. Combined with AI algorithms, it can automatically issue alarms and pause equipment.
Campus safety: Monitor school bullying and abnormal student behaviors (such as prolonged stay in dangerous areas), and link with the access control system and parent-side APP for real-time warnings.
Energy management: Monitor energy consumption data in the park (such as the usage of lights and air conditioners) through cameras and sensors, optimize energy allocation, and achieve green energy conservation.

Smart Park
(3)Intelligent Transportation:
Highway/Railway: Use video analysis technology to identify traffic accidents and road obstacles, and release early warning information in real time through variable message signs; monitor and remind drivers of fatigued driving, distracted driving and other behaviors.
Intelligent parking lot: Automatically complete vehicle entry and exit billing through license plate recognition, and recommend vacant parking spaces by combining AI algorithms to reduce parking waiting time.
(4)Smart Home/Community:
Home security: Intelligent cameras support facial recognition for unlocking and alarm for abnormal intrusion, allowing real-time monitoring of home conditions through a mobile APP; linking intelligent door locks, smoke alarms and other devices to build a whole-house security system.
Community management: Monitor violations such as elevator overloading and electric vehicles being charged indoors, use AI voice to dissuade and notify property management; analyze community waste classification data to optimize waste collection routes.
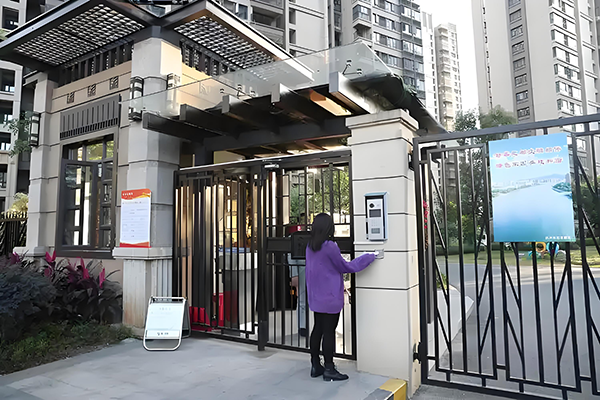

Smart Community
4.Core Advantages and Characteristics
(1)From "passive monitoring" to "active early warning":
Traditional monitoring relies on manual review of videos, while intelligent monitoring uses AI algorithms to automatically identify anomalies and trigger warnings (such as smoke detection in the early stages of a fire, automatic alarm for elderly falls), shortening the response time.
(2)Multi-dimensional Data Fusion:
Integrate multi-source data such as videos, sensors, and GPS trajectories to provide more comprehensive scenario analysis (e.g., predict peak passenger flows in scenic spots by combining weather data and deploy security forces in advance).
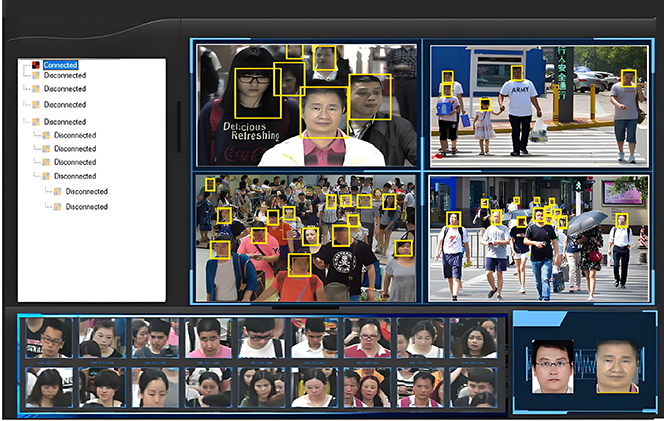
AI Recognition and Early Warning
(3)Automation and Intelligence:
Reduce manual intervention, such as: intelligent analysis of out-of-stock items on shelves and automatic replenishment (retail scenarios), AI-based identification of power equipment failures and dispatch of maintenance work orders (energy scenarios).
(4)Scalability and Cost Optimization:
Based on a cloud computing architecture, it supports large-scale device access and functional expansion; AI algorithms reduce reliance on manual inspections, saving long-term operation and maintenance costs.