导航栏
The "QAIT" company has deep expertise in the power industry, focusing on the field of power facilities, and professionally provides power generation equipment, power supply equipment, and supporting planning services. Its equipment products cover transformers, transmission and distribution facilities, high-voltage switchgear, insulating materials, electrical control systems, etc.; the service scope includes substation construction planning, transformer maintenance plant construction planning, etc., providing integrated solutions for the construction, operation and maintenance, and upgrading of power facilities through a full-chain business system.
1.Power Facilities Overview:
"Power facilities" refer to the general term for various equipment, devices, buildings, and structures required in the links of power generation, transmission, transformation, distribution, and consumption. They serve as the material foundation to ensure the safe, stable, and efficient operation of the power system.
2.Power Facilities type:
(1)Electrical primary equipment: Equipment directly involved in the production, conversion, transmission, distribution, and consumption of electrical energy.
Electrical energy production and conversion equipment: Such as generators, motors, transformers, etc. Among them, generators convert other forms of energy into electrical energy, motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, and transformers are used to change voltage levels to meet different power demand.

Transformer
Switching appliances: Such as circuit breakers, disconnectors, contactors, fuses, etc., which are used to connect and disconnect circuits, and control the transmission and distribution of electric power.
Current-carrying conductors and gas-insulated equipment: such as busbars, power cables, insulators,wall bushings and so on, are used to transmit and distribute electric energy, and ensure the insulation performance of electrical equipment.
Devices for limiting overcurrent or overvoltage: such as current-limiting reactors, lightning arresters, etc., are used to limit overcurrent and overvoltage in the circuit and protect the safe operation of electrical equipment.
Instrument transformer equipment: such as voltage transformers and current transformers, which reduce the high voltage and large current in the primary circuit for the use of measuring instruments and relay protection devices.

Voltage Transformer (VT)
(2)Electrical secondary equipment: Equipment used to measure, monitor, control, and regulate the operating status of primary electrical equipment to ensure its normal operation. It mainly includes various measuring instruments, various relay protection and automatic devices, DC power supply equipment, etc.

Electrical Control Cabinet
3.Common Electrical Equipment:
(1)Power Generation Equipment
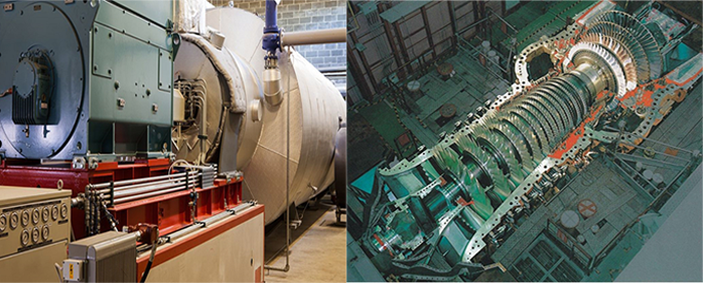
Power Station Boiler and Steam Turbine
Power station boiler: It is a device that uses the thermal energy released by fuel combustion or other thermal energy to heat the working medium water or other fluids to certain parameters, and the generated high-temperature and high-pressure steam is used to drive the steam turbine.
Steam turbine: It drives the impeller to rotate through steam, converts the thermal energy of steam into mechanical energy, and then drives the generator to generate electricity.
Hydraulic turbine: It uses the energy of water flow to drive the runner to rotate, converts the potential energy and kinetic energy of water into mechanical energy, and then drives the generator to generate electricity, which is common in hydropower stations.
Generator: It is a device that converts other forms of energy into electrical energy. Common types include thermal generators, hydraulic generators, wind generators, solar generators, etc.
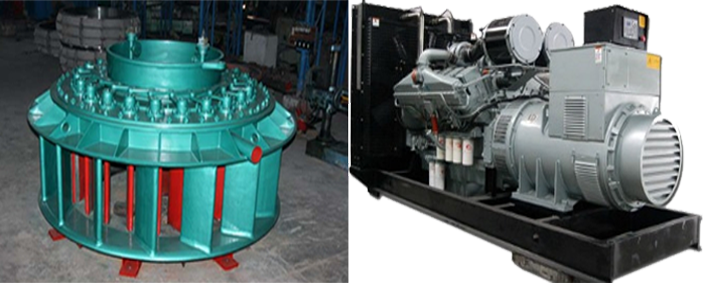
Hydraulic Turbine and Generator
(2)Power Supply Equipment
Transmission line: It is used to transmit the electric energy generated by the power plant to the substation or the user side. According to the voltage level, it can be divided into high-voltage transmission line, extra-high-voltage transmission line, ultra-high-voltage transmission line, etc.

Transmission Facilities
Transformer: Including voltage transformers and current transformers, which are used to measure the voltage and current in the circuit and provide signals for measuring instruments, relay protection devices, etc.
Contactor: It is an electrical appliance used for remotely and frequently switching on and off AC/DC main circuits and large-capacity control circuits, mainly for controlling equipment such as motors, welding machines, and capacitor banks.
Annex 1. Substation Construction
"Substation" is a power facility in the power system that transforms voltage, receives and distributes electric energy, controls the flow of electricity, and adjusts voltage. It is mainly composed of transformers, busbars, switching equipment, instrument transformers, relay protection devices, capacitors, and other electrical equipment. Substation construction is a complex systematic project that needs to strictly follow relevant standards and specifications to ensure construction quality and safety, so as to meet the requirements of stable operation of the power system and power supply reliability.

Substation Construction
(1)Pre-planning and Site Selection
Planning: According to the regional power development needs and grid planning, determine the main parameters of the substation, such as voltage level, capacity, number of outgoing lines, etc. At the same time, consider the connection mode between the substation and surrounding power sources, load centers, as well as its impact on the entire power grid.
Site Selection: Select areas with stable geology, high terrain, and less vulnerability to natural disasters such as floods. Consider convenient transportation to facilitate the transportation of equipment and the access of construction vehicles. At the same time, it should be kept away from environmentally sensitive areas such as residential areas, schools, and hospitals as much as possible to reduce the impact of electromagnetic radiation and noise on surrounding residents. In addition, the coordination with urban planning should also be considered to avoid building substations in reserved land for urban development or important landscape areas.
(2)Design Stage
Electrical Design: It includes main wiring design, short-circuit current calculation, equipment selection, etc. The main wiring design should meet the requirements of reliability, flexibility, and economy, and select appropriate wiring modes such as single busbar section, double busbars, etc., according to the functions and load characteristics of the substation. The short-circuit current calculation is carried out to determine the rated parameters of electrical equipment, ensuring that the equipment can operate safely and reliably during short-circuit faults. Then, electrical equipment such as transformers, switching equipment, busbars, and instrument transformers are selected based on the calculation results and operation requirements.

High-voltage switchgear assembly equipment
Civil Design: According to the layout requirements of electrical equipment and on-site topographical conditions, carry out the general plane layout design of the substation, and reasonably divide the production area, living area and auxiliary area.
Carry out structural design for buildings and structures to ensure that they can bear loads such as equipment weight and seismic force. At the same time, design auxiliary facilities such as water supply and drainage, ventilation and fire protection to meet the operation and safety requirements of the substation.
(3)Construction Process
Foundation Construction: First, carry out site leveling and foundation excavation, and pour equipment foundations, structure bracket foundations, etc., according to design requirements. During the foundation construction process, strictly control the dimensions and elevation of the foundation as well as the casting quality of concrete to ensure the stability and reliability of the foundation.
Electrical Equipment Installation: After the foundation construction is completed, the installation of electrical equipment is carried out. In accordance with the equipment installation manual and construction specifications, equipment such as transformers, switching equipment, busbars, and instrument transformers are installed in sequence, and the connection and debugging between the equipment are performed. During the installation process, attention should be paid to the installation accuracy and connection quality of the equipment to ensure the normal operation of the equipment.
Line Erection: Carry out the erection of incoming and outgoing lines of the substation, including overhead lines and cable lines. For overhead lines, pay attention to the erection of towers, the laying of conductors, and the adjustment of sag; for cable lines, pay attention to the laying of cables, the production of joints, and the installation of cable terminals. At the same time, implement safety measures such as lightning protection and grounding for the lines.
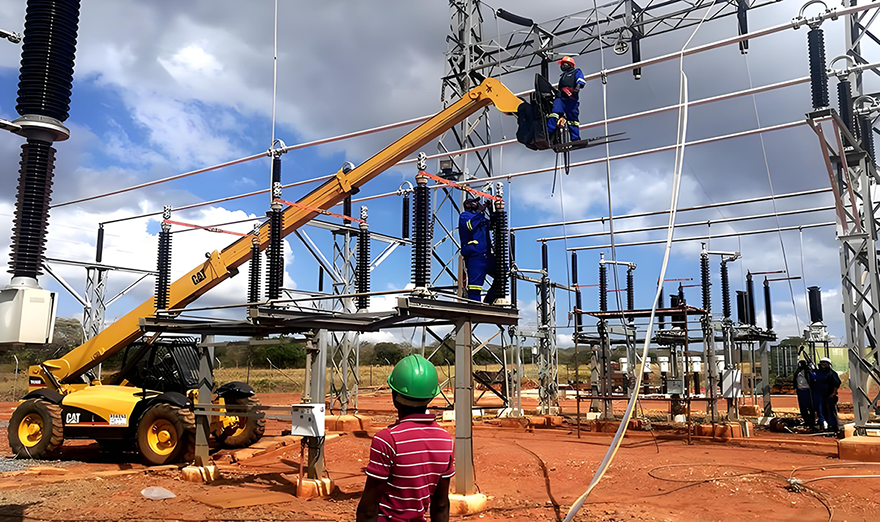

Line Erection
Civil Engineering Construction: The construction of buildings and structures of the substation shall be carried out simultaneously, including the construction of houses such as the main control building, power distribution room, and capacitor room, as well as the construction of auxiliary facilities such as walls, gates, and roads. It is necessary to ensure the construction quality and aesthetic appearance of the buildings to meet the operation and management requirements of the substation.
(4)Commissioning and Acceptance Stage
Commissioning: After the installation of equipment is completed, system commissioning is carried out, including single-unit commissioning, sub-system commissioning, and overall commissioning of electrical equipment. Through commissioning, check whether the performance of the equipment meets the design requirements, whether the operation of the system is stable and reliable, and identify and solve the problems existing in equipment installation and system connection.
Acceptance: After the commissioning is completed, relevant departments and experts shall be organized for acceptance, including the acceptance of civil engineering, electrical equipment, system functions, etc. During the acceptance process, inspections and tests shall be carried out in strict accordance with relevant standards and specifications, and the identified problems shall be rectified in a timely manner to ensure that the construction quality and safety performance of the substation meet the requirements. The substation can only be put into operation after passing the acceptance.
Annex 2: Construction of Transformer Maintenance Plant
(1)Pre-planning and Site Selection
Market research: Understand the demand, competition status, and future development trends of the transformer maintenance market in the local and surrounding areas, including the quantity of various transformers, voltage levels, service life, failure frequency, etc., to determine the market positioning and service scope of the maintenance plant.
Determine the scale: Based on the market research results, and combining conditions such as funds and site, determine the scale of the maintenance plant, including the area of the maintenance workshop, equipment configuration, number of personnel, etc. For example, a small-scale maintenance plant may mainly focus on low-voltage transformers, while a large-scale maintenance plant needs to have the maintenance capability for high-voltage and extra-high-voltage transformers, and accordingly requires a larger site and more advanced equipment.
Site Selection:
Convenient transportation: It should be convenient for the transportation of transformers and the access of equipment and materials, preferably close to highways or railway freight stations.
Close to the market: Try to be close to the area where transformer users are concentrated to reduce transportation costs and response time.
Environment suitability: Choose a place with high terrain, dry and good ventilation, avoid inflammable and explosive sites and densely populated areas. At the same time, consider the development plan of the surrounding environment to avoid possible interference and demolition in the future.
Layout Design: Reasonably plan functional areas such as maintenance workshops, parts warehouses, office areas, and test sites according to the maintenance process and equipment configuration. The maintenance workshop should be spacious enough to meet the disassembly, assembly, and maintenance operation requirements of transformers of different specifications; the test site should have a good electromagnetic environment to ensure the accuracy of test data.
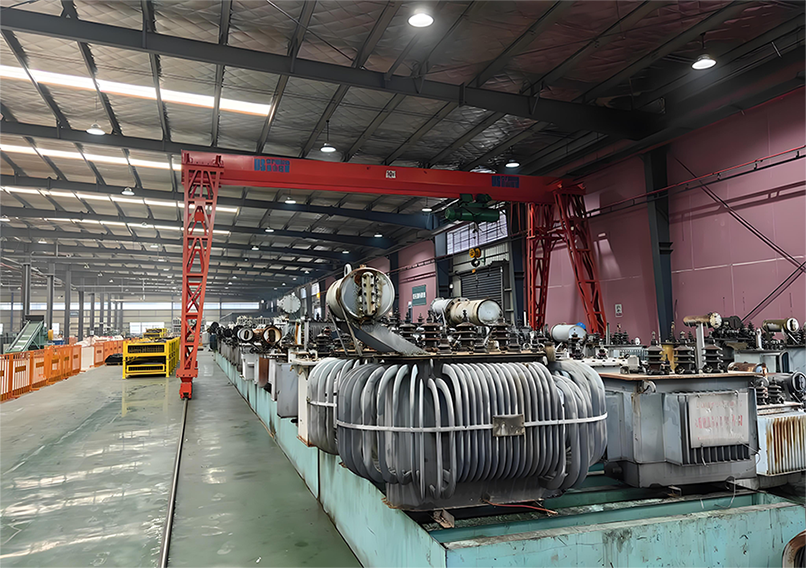

Transformer Maintenance Plant
(2)Funding Budget
Construction costs: including land acquisition or lease fees, factory construction or renovation costs. For new factory construction, requirements for building structure, area, fire protection, etc., should be considered; if leasing a factory, a suitable site should be selected according to the scale and needs of the maintenance plant, and necessary decoration and renovation should be carried out.
Equipment procurement: including testing equipment such as test transformers, megohmmeters, turns ratio testers, winding deformation testers, as well as maintenance tools and equipment such as cranes, welding machines, and winding machines.
Personnel costs: cover expenditures on recruitment, training, salaries and benefits, etc. According to the scale and business scope of the maintenance plant, recruit electricians, electrical engineers, technical workers and other personnel with professional skills, and arrange induction training for new employees and regular skill improvement training.
Operating funds: Set aside a certain amount of operating funds for purchasing spare parts and components required for daily maintenance, paying water and electricity bills, office expenses, etc., and for addressing possible capital turnover issues.
(3)Equipment and Technology
Equipment selection: According to the service scope and technical requirements of the maintenance plant, select appropriate detection, maintenance equipment and tools. The equipment should have high precision, reliability and safety. At the same time, the cost-performance ratio of the equipment and after-sales service should be considered.
Maintenance equipment: Equipped with professional transformer maintenance equipment, such as lifting equipment (traveling cranes, overhead cranes, etc.), winding equipment, drying equipment, vacuum oil purifiers, and electrical test equipment (such as withstand voltage testers, turns ratio testers, winding DC resistance testers, etc.).
Tools and instruments: Prepare various special tools, such as wrenches, screwdrivers, power tools, hydraulic tools, etc., as well as detection instruments, such as infrared thermal imagers, ultrasonic detectors, etc., for fault detection and maintenance quality inspection.
Technical support: Cooperate with transformer manufacturers, scientific research institutions or professional technical teams to obtain technical support and training,
so as to improve the technical level of the maintenance plant and the ability to solve complex problems. In addition, a perfect technical document archive should be established, and relevant technical drawings, maintenance manuals, standards and specifications of transformers should be collected to provide references for maintenance work.
(4)Parts Supply and Management
Parts Inventory: Establish a sound parts inventory management system, and stock common transformer parts such as windings, iron cores, insulating materials, tap changers, bushings, etc., to shorten the maintenance cycle. At the same time, establish long-term cooperative relationships with multiple parts suppliers to ensure timely access to special or customized parts when needed.
Quality Control: Carry out strict quality inspection on purchased parts to ensure they meet the technical requirements and quality standards of transformers. Establish a parts quality traceability system to enable timely tracing and handling of parts with quality problems.
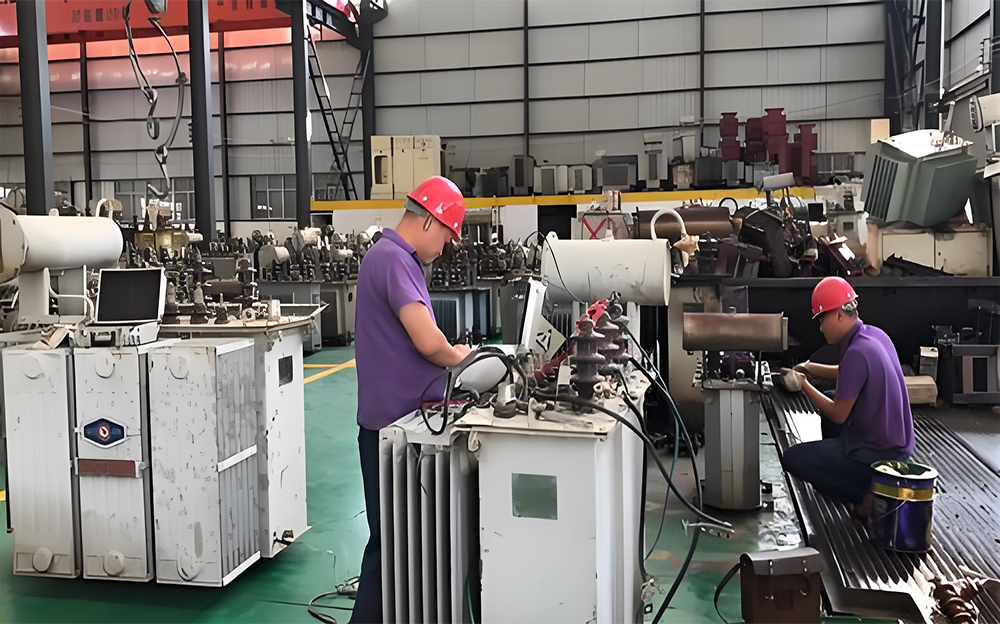

Transformer Overhaul
(5)Staff Recruitment and Training
Staff Recruitment: On the one hand, recruit engineers and technical workers with rich experience in transformer maintenance, covering positions such as electrical engineers, mechanical engineers, electricians, winding workers, and testers. These technicians should be familiar with the working principles, structural characteristics, and maintenance processes of transformers, and must possess relevant qualification certificates and work experience, such as high-voltage work operation certificates, electrical equipment installation and commissioning worker certificates, etc. On the other hand, recruit some management personnel and logistics staff to be responsible for the daily operation and management of the maintenance plant.
Staff Training: Regularly organize employees to participate in professional skills training to learn the latest maintenance technologies and process standards, and conduct skills assessments to ensure that employees have good professional standards and operational skills.
(6)Safety Management and Environmental Protection Measures
Safety Management: Formulate strict safety management systems, strengthen safety training for employees, and enhance safety awareness. Set up safety warning signs in maintenance workshops and test sites, and equip necessary safety protection equipment and fire-fighting facilities to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment during maintenance.
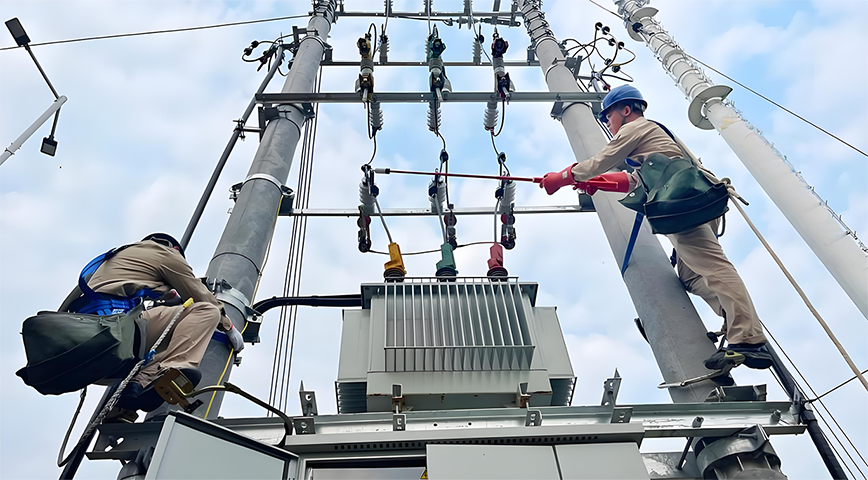

Line Maintenance
Environmental Protection Measures: Adopt effective environmental protection measures to reduce waste emissions and environmental pollution during maintenance. For example, classify, recycle, and dispose of waste oil, used insulating materials, and other waste to prevent soil and water pollution; reasonably control noise and dust emissions during maintenance to protect the surrounding environment and the quality of life of residents.
(7)Quality Management, Certification Qualifications and After-Sales Service
Quality Management: Establish a sound quality management system, and formulate maintenance process flows, quality control standards, and inspection specifications. Carry out strict quality control and inspection throughout the maintenance process. Transformer after maintenance should undergo rigorous testing and trials to ensure that all performance indicators comply with relevant national standards, industry codes, and customer requirements.
Certification and Qualifications: Actively apply for relevant quality management system certifications, such as ISO 9001 quality management system certification, and qualification certifications in the power industry, such as the License for Installation (Maintenance, Testing) of Electrical Facilities, so as to enhance the market competitiveness and credibility of the maintenance plant.
After-sales service: Establish an after-sales service team to promptly respond to customers' after-sales needs, and provide warranty services and technical support after maintenance. Regularly follow up with customers to understand their satisfaction with maintenance services and their opinions and suggestions, so as to continuously improve service quality.